- Label where to start more clearly
- Simplify rule wordiness
- Make the outline colors on the board dots more prominent
- player count?
- Make spaces bigger to accommodate multiple players being on one spot
- The left and right moving on the game board is a good idea, but I would like to see more directional cues on the board.
- How to win is a little confusing because you get to choose which path to take when you start instead of having the choice made for you. If winning meant being the farthest left on the game board, then i would choose to move left every time to win.
- I like the name of the game and i think you should add more details and or facts about why you chose it and add in that you picked counterclockwise game play because thats the way the earth spins.
- Looking at the board now, there is no indication that the game has anything to do with earth, maybe add a couple more graphics
Hues and Cues Game Review
I enjoy this game but it really shows how limited my vocabulary is and how slowly I can think on the spot. Evelyn mentioned when she played before all players took turns putting their pieces on the board instead of all at once. I like how we all rushed at once because it adds a more competitive aspect to the game. I think it also makes the game go faster when you have a lot of players.
My frustration with this game is that the card colors do not match the game board colors very well. I think if you are making a hues game with a lot of color variation, you better make sure the colors match correctly. I think they should really fix that because you have to look at the board code color when you are giving cues and people can tell where you are looking if you are not strategic.
I like how you get points for how many people got in the square when you care giving cues. It makes the hinter really want to think of good words because it benefits them when the other players go good.
Also I wished the board laid more flat when playing but thats just me being picky.
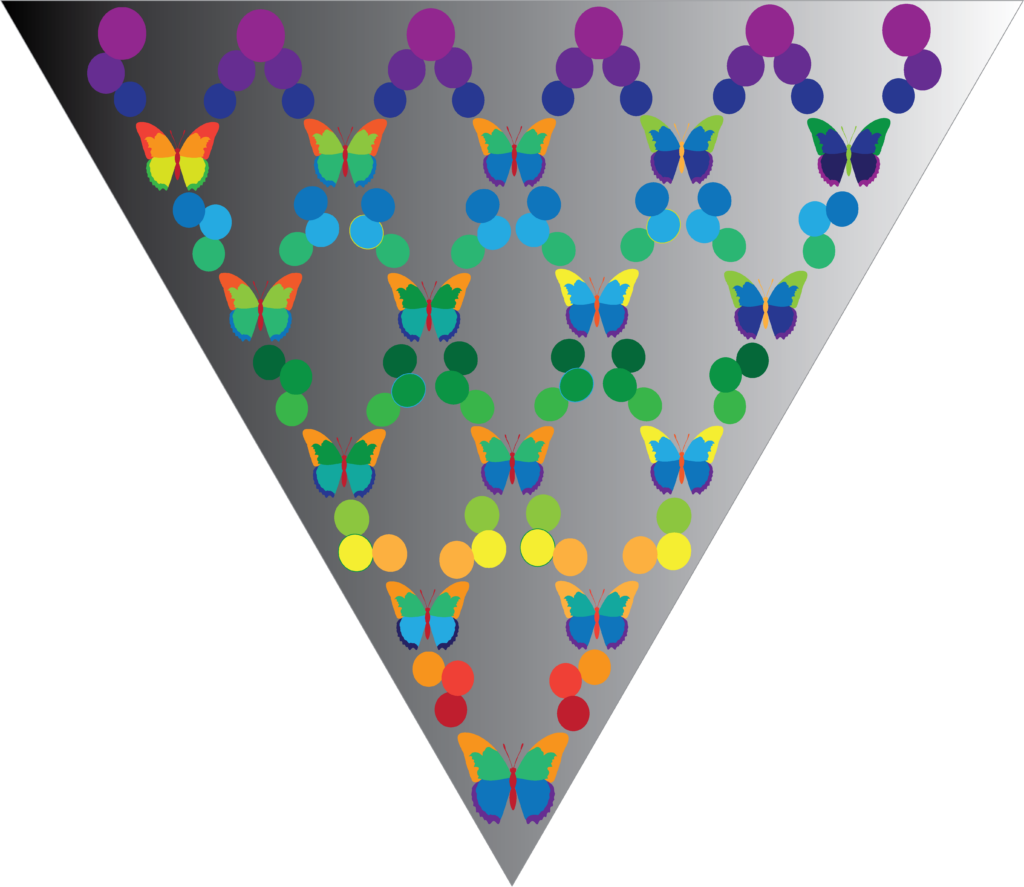
Obstruction – Harding
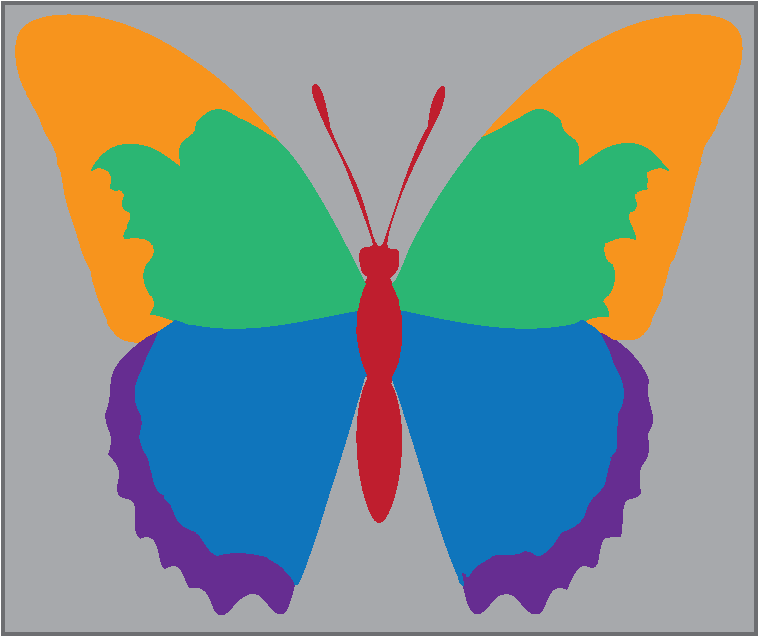
the butterfly effect
Players are moving on a board where they have to answer questions at certain points of the board, changing course with each action affecting what their actions could do to the world.
4 players
3 sided die
cards
Boost cards
Players will start their pieces on the planet in the button of the board.
The player that is the oldest will roll the die first and the play moves counterclockwise.
Players move as many spaces as the dice shows.
When a player lands on an impact space marked by the butterfly they must pick up a butterfly card and answer the question yes or no and explain why, it doesn’t need to be every reason, just a few so the group can agree with them or disagree with the player. When a consensus is reached follow the arrow for either yes or no from the card.
If you land on the impact spot in the middle of your move then answer and continue your move.
If a player lands on a charity space(circle spaces with a different outline color) at the end of their move, they can pick up a boost card that counts at the end of the game so keep it until everyone has finished.
The point of this game is not to make it first, it is to see your impact. When every player has reached the finish line, look at how you fared in changing the world. A charity card lets you move over one finish to the left. Whoever is closest to the “ideal world”(farthest left finish) wins the game.

Barrel of Truth Game Review
- What was the most frustrating moment or aspect of what you just played?
- I think that the only thing that frustrated me with the game was the fact that the players were sometimes nudged in criticizing each other. Regardless if it is up to us to take the game in any direction, I feel that some questions could easily turn people against each other. The thing is, if I were playing with a group of people that didn’t like me, it would be easy for them to answer questions in a negative manner.
- What was your favorite moment or aspect of what you just played?
- The game was a very good way of getting to know people better, as well as learning about what people think about me. I enjoyed the interactions from this game, as well as thinking of funny things to say on my response cards. There was also a neat sense of randomness in which I didn’t know what to expect from people.
- Was there anything you wanted to do that you couldn’t?
- I wanted to draw pictures, as well as seeing other pictures that people could draw. I think that drawing prompts would contribute to more funny/interesting interaction.
- If you had a magic wand to wave, and you could change, add, or remove anything from the experience what would it be?
- Bouncing off of the previous question, I’d add drawing prompts, which would spice up the playing experience. It would be hilarious to try to guess who drew a certain picture, almost like JackBox. If I could change anything, I would change a couple of the questions that might cause controversy. Based on what I said in the first question, maybe you could reword the prompts to make it less personal. Lastly, I think that it would be cool to incorporate a timer during the playing experiences so that people don’t have to wait on each other to finish.
- What should be improved with the next version?
- The game is already really fun, and doesn’t need a whole reiteration. I think that the prompts can be misinterpreted, as I’ve talked about how sometimes it can feel personal. Other than that, I think that by adding a few things I’ve talked about, you could boost the potential of this game.
- What was the game’s message?
- It is kinda hard to tell what the message of the game is, but I’d have to say it is about trust. It can show the true colors of people (responding to prompts anonymously) so you just have to trust that you are playing with friends not foes.
- Describe the game in 3 words.
- Social, trusting, funny
Pixel sprite art
Slim Jim Ad
I apologize for the video quality but I thought this was so ironic, Slim Jim just released an game advertising their products. I might download it, let me know if anyone has played it yet!
Final Game Research?
For my final game, I really wanted to try to make a video game, so I’ve conducted a little bit of research about various video game making software and applications. I really would like to make a choose-your-own-adventure game, something that is super narrative and text-based. So I started looking up the best platforms to make stuff like this and this is what I came up with. If anyone has any other suggestions for what I could use, I greatly appreciate it!
- Text Adventures
- Or I could easily code my own version in HTML (probably)
- https://jams.hackclub.com/jam/story-game
- This article seems super helpful
- It uses https://replit.com/
- https://codesandbox.io/p/sandbox/choose-your-own-adventure-game-y9xc0
- Twine – Interactive Fiction
- Examples of games I really enjoyed made by this software:
- https://idrellegames.itch.io/wayfarer
- https://litrouke.itch.io/a-man-outside – horror game SO GOOD
- https://artsybarrels.itch.io/goodbye – game about saying goodbye and suicide. so good
- https://ghoulnoise.itch.io/thereliefofimpact – game about sleep paralysis
- https://yllogique.itch.io/its-a-beautiful-day – a game about self care
- https://direkris.itch.io/you-are-jeff-bezos – a game about spending a day as Jeff Bezos and it really makes you realize how much money he really has
- Examples of games I really enjoyed made by this software:
- Unity
- Unreal Engine
Game Reviews
As part of my exploration for this game, I also played various interactive fiction type games, specifically ones that were made using Twine. Twine is a big contender for what I will use to make this game, as it is mentioned a lot online and I really like some of the games that people have created using it. I highly recommend playing some!!
A Man Outside – https://litrouke.itch.io/a-man-outside
- Was it fun? Yes! And very suspenseful at that! I was super impressed with the way the game was made as well.
- What were the player interactions? As a single player game, the player did have the chance to interact with other “characters”. There was a text conversation going on between you and your friend, regarding the man standing out your window. The friend would check in on you and it helped escalate the game.
- How long did it take to learn? I learned this game almost instantly. With the help of little notes and flashing symbols indicating what to click, it made it very easy to grasp.
- Would you play it again? Yes, I would, especially to see if there were any other endings that I missed. I also wasn’t able to play with sound for my first playthrough and I think that would really add to the game experience.
- Analyze the game using the 3 act structure. Act 1: text conversation with your friend begins. You discuss about how you need to study on your vocabulary app, but there is a weird guy who has been standing outside your window for a long time. You complete the first set of vocabulary flashcards on your phone. Act 2: the man is still there, and you move on to work on the second set of vocabulary flashcards. The flashcards start to glitch a little bit and some of the words have creepy definitions, and the tension really starts building. Act 3: the man is still there (at some point he does disappear though). Your friend gets worried and you have to make the decision to either call your mom or ask your friend to drive there. I asked my friend to drive there, but before she got there, the man disappeared and I heard a sound in the house. I thought it was my friend but when I went to go investigate, I presumably died and had the “bad ending”.
- What is the game’s metaphor and which of the game’s mechanics standout? This is a horror game about trying to do your school homework, but there is something that threatens your safety outside, however you are persistent to finish your homework, but it can lead to your demise. I thought it was super interesting to have the player actually go through the vocabulary flashcards. The glitching moments of that were also super cool and made it very suspenseful.
- What was the most frustrating moment or aspect of what you just played? It felt like some of the cards took forever to load up or assess if I was right or wrong, but I’m pretty sure that that was intentional to add to the anxiety and suspense.
- What was your favorite moment or aspect of what you just played? My favorite aspect of the game was the subtle details in the vocabulary cards. The definitions seemingly reflected the situation that you were in at times and were actually quite challenging to answer. (It also let you pick your vocabulary level and I thought that was a nice touch!)
- Was there anything you wanted to do that you couldn’t? I don’t think there was a way to go back to the text conversation without exiting the vocabulary app altogether and losing your progress, so I wish I could have done that.
- If you had a magic wand to wave, and you could change, add, or remove anything from the experience, what would it be? I think I would have enjoyed more emphasis on the text conversation.
- What should be improved with the next version? Very little! Maybe more alternate endings?
- What was the game’s message? Homework can wait. Prioritize your safety.
- Describe the game in 3 words. Suspenseful, educational, dark
Goodbye – https://artsybarrels.itch.io/goodbye (depression and suicide warning)
- Was it fun? I enjoyed the game, but I’m not sure I would call it fun. It’s a little too sad a subject for that.
- What were the player interactions? The player got to make decisions that determined the actions of their character. The player was also able to interact with other characters, most notably, the mom, as they are on their way to end their life. In certain paths of the game you also have the opportunity to call other characters such as your sister, dad, or friends to say your goodbyes.
- How long did it take to learn? Games like this are pretty intuitive so I understood it pretty much instantly.
- Would you play it again? Yes, I would like to go through all of the different storylines and endings.
- Analyze the game using the 3 act structure. With a game like this, the 3 act structure is going to change based on your actions. The 3rd act in some of the playthroughs ends with your character ending their life, and the others you decide not to. But generally the first act is how are you going to start the day that you intend on ending your life (will you shower, clean your room, etc.) and then the 2nd act is when you go downstairs and have to say something to your mom as you are leaving. This is a pretty pivotal point in the game as your mom notices that something is wrong and here is where you may select a choice that will convince you to not end your life.
- What is the game’s metaphor and which of the game’s mechanics standout? The game’s metaphor is about depression, suicidal thoughts, with a big emphasis on saying goodbye to people before you end your life. The mechanics themselves weren’t necessarily anything special, but I really liked the touch of being able to select who to say goodbye to in the one ending.
- What was the most frustrating moment or aspect of what you just played? I think the frustration I experienced was mostly out of anxiety of not knowing what was going to happen. It is frustrating because you don’t want to think about someone ending their life and frustration about what your family members have to say in their last conversation with you. It was all intentional.
- What was your favorite moment or aspect of what you just played? The art style of this game was beautiful, and I think they really portrayed a scenario like this well. It definitely had me in my feelings.
- Was there anything you wanted to do that you couldn’t?
- If you had a magic wand to wave, and you could change, add, or remove anything from the experience, what would it be? Not really!!
- What should be improved with the next version? Maybe slightly more interactivity or choices? But I also don’t want it to become unrealistic for a person who is battling depression.
- What was the game’s message? Saying goodbye to loved one’s before you end your life. (very well done!!)
- Describe the game in 3 words. Beautiful, heart-wrenching, poetic
Case Study – We Didn’t Start the Fire
Short Summary
We Didn’t Start the Fire is a song from 1989 by Billy Joel. It contains references to popular culture and newsworthy, significant events from around the world and the United States (over 100 references mentioned). In 2023, Fall Out Boy released an updated version of We Didn’t Start the Fire, with events from 1989-2023 (over 80 references mentioned).
In the game version, players answer trivia questions about history and pop culture from the time period of either song. When players answer questions correctly, they are able to move their token closer to the fiery finish line.
The purpose of this game is to make a fun reference to the songs, and also provide context and background information to some of the lyrics. It is important to be educated about both world history and culture.
Primary Audience: Billy Joel & Fall Out Boy fans, history/pop culture enthusiasts
Other than the primary audience, I feel like this game could be enjoyed by a large number of people. Trivia games have pretty mass appeal to people, so someone that enjoys a trivia game would enjoy this game.
Design Process & Thought Process
Iterative Design: For the design of this game, I kept a red, black, and white color palette. I wanted to have experimental typographic lyrics on each of the cards so that players can refer to the lyrics that the trivia question pertains to. I varied the typography by using varying weights, as well as oblique and italic type. The backs of the cards have photoshopped pictures of either Billy Joel or Fall Out Boy, in a context that I felt pertains to the game (either from the music video or pictured with fire). The fronts of the cards have a red gradient behind the lyric typography, with a black box that contains the trivia question.
For the future, I would like to continue working on the design of this game. I need to redraw the images of Fall Out Boy and Billy Joel so that it will work better for copyright purposes. This will also help me get a more unifying style for my game. I likely want to keep the same color palette, but I could also explore using blue flames as well. The typography also needs some refining, and I want to fit all of the lyrics into one unified block, keeping all of the varying weights. I would also consider having different card backs (maybe with just different pictures of the artists), just to make it a little more visually exciting.




Game Mechanics: Players pick up cards, answer trivia questions, and discard cards when they are done. The players advance their player token when they answer a question correctly.
Player Goals: In the first iteration, the players goals were to be the first player to reach the end of the board. This is accomplished by answering 5 trivia questions correctly. I would like to make this number a little bit higher in the future, or potentially have it adapt depending on the number of players. I would also consider making a game board with spaces that make you pick up the trivia cards versus picking up a trivia card on every single turn.
Gameplay Sequence: The sequence of gameplay is as follows: decide who goes first, another player picks up the card for the player whose turn it is and asks them a trivia question, if the player answers correctly they advance forward on the game board, it cycles to the next player’s turn. The first player to get to the end of the game board wins and the game ends.
Game Board & Components: In the current game board, players start at the top and move linearly down to the bottom of the board, moving one step with each card they answer correctly. In future iterations, I would like to add more tiers to this game board and consider a nonlinear path that players could potentially follow.

Rulebook and Playtesting
Rulebook Sample:
Playtesting Notes: Overall, from playtesting, I learned that this game is a feasible idea. Players enjoyed the trivia questions and learning more about history and culture. No major frustrations presented themselves throughout the game, but I feel as though I could still make the game more interesting and exciting for future players.
- What questions did your players have? The game was pretty straightforward so there weren’t a lot of questions. I think the questions were mostly about the song itself and some of the pop culture and history questions.
- How quickly did they learn to play? The players learned extremely quickly since it was a simple trivia game.
- What kinds of interactions did the players have? Players discussed the different historical and pop culture events and asked each other and answered questions.
- What confused players? The only thing that was confusing was having to keep track of your own points and keep the card that someone else asked you about.
- What made players excited? Players were excited to answer questions, get questions correct,etc.
- What did your players enjoy doing? They enjoyed answering the questions. They enjoyed the challenge of it and some of the questions provided a good discussion.
- Did any aspect of the game frustrate players? Players didn’t have any frustrations.
Game Reflections: Developing this game allowed me to learn more about history and culture myself, as I was developing the game I didn’t know a lot about the topics that were mentioned in the songs. Next time, I would probably develop this concept a little more to make it go beyond a trivia game, like including some unexpected elements or not having each player’s turn be exactly the same. I also didn’t anticipate that players would want to continue answering questions beyond the 5 card winning point, and I thought they would have gotten sick of the same format, but surprisingly, they really didn’t and wanted to continue answering the questions.
Game Reviews/Playtests
Evelyn’s Around the World in 80 Days
This was a great game and I could see myself playing this with my family!
1. What was the most frustrating moment or aspect of what you just played? It was frustrating playing with so many people. It took a long time to get to my turn, and we weren’t able to finish the game. But that’s not really an issue with the game’s rules though!
2. What was your favorite moment or aspect of what you just played? I like the cards where everyone has the chance to participate, like with naming all the countries that start with a certain letter.
3. Was there anything you wanted to do that you couldn’t? Not that I can think of.
4. If you had a magic wand to wave, and you could change, add, or remove anything from the experience, what would it be? Maybe make the board a little more exciting. I feel like for the type of the game it is, a square board just feels a little boring, but I wouldn’t be mad if it wasn’t changed at all!
5. What should be improved with the next version? I’m not sure how I feel about the blank spaces on the board, part of me wants something to be there but I’m not sure. Maybe some of the trivia cards could have some stuff about capital cities as well?? You could also include some more visual-oriented cards like country flags, fashion, etc.
6. What was the games message? The game was about culture and geographic education.
Evan’s Cracking Jokes Game
This was a pretty fun game! I could see myself playing this with friends!
1. What was the most frustrating moment or aspect of what you just played? It was just a little too unstructured for me. I feel like I need a timer or a way to keep track of who is “winning”.
2. What was your favorite moment or aspect of what you just played? I enjoyed cracking the glowsticks, telling jokes, and listening to what everyone came up with.
3. Was there anything you wanted to do that you couldn’t? I wanted some of the jokes to be something where the whole group had to tell a joke with that category.
4. If you had a magic wand to wave, and you could change, add, or remove anything from the experience, what would it be? Just adding things to switch up the turns so it’s not just pick up a card, tell a joke, and repeat.
5. What should be improved with the next version? You could consider adding the idea of having a spinner or something that determines if the whole group was gonna tell a joke, if it would just be one person, or maybe their is a “duel” with two people? I think that something like that could help make the game a little more exciting (don’t get me wrong I love this game though!) I also wonder if there is an alternative to the glowsticks that you could use so that it isn’t as wasteful?
6. What was the games message? Telling jokes, making others smile?
3 Minute Obstruction – Mathews
Prototype 3 – “Sustainable City Builder”
Around the World in 80 Days – Prototype 2 Playtest
Changes from GameTest 1 to 2
- Group vote for mispronunciation
- harder phrases to learn
- shorter timer to memorize timer
- Incentive to read culture cards? People aren’t reading
- Changed the end of the game from reaching 10 culture cards to returning back to home.
- Added 3x more phrases, trivia, and group cards.
- Added multi choice
Playtest 2 notes: 9 people played
Changes I will make for the next prototype:
I need to LABEL CULTURE CARDS
Change trivia card format – Put answer on the back of the card.
Tweak the group game mechanics. People can drop out of remembering a country. If players pass, pass until the next player knows them. If you pass, you are out. Also, if players challenge a country stated in this mini game, the player who landed on the space can google it.
North Korea is not on the Group Cards for “n”
Greenland is technically not a country… but everybody thinks its a country. Perhaps add a loophole that if majority thinks a “territory” is considered a country, it can count. This is only relevant if players challenge a country within the Group Game
Add back an alternative ending – now, to win, it’s the first player to 7 culture cards or when a player gets back to start.
Maybe add trivia cards for how to say a country’s name in their native language
I will add a player cap of 8
Game Rules for “Sustainable City Builder”
Review on Evelyn’s Game
- What was the most frustrating moment or aspect of what you just played? Trying to think of countries that started with a particular letter when I was first to go.
- What was your favorite moment or aspect of what you just played? I loved listing to other players trying to pronouce phrases in other languages.
- Was there anything you wnated to do that you couldn’t? No not at all, this game is perfect.
- If you had a magic wand to wave, and you could change, add, or remove anything from the experience, what would it be? I would mention something about reading the culture cards because I feel like some people would’ve missed that.
- What should be improved with the next version? Nothing
- Describe the game in 3 words. Fun, challenging, educational














